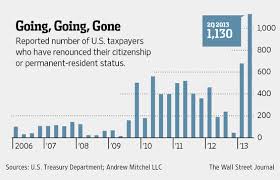
In the face of increasingly strict asset disclosure legislation, more and more United States citizens are renouncing their citizenship in order to avoid potential tax consequences. In the second quarter of this year, the number of expatriates turning in their passports to United States embassies abroad was up almost 500% from that same time period the previous year. Compared to the first half of 2008, the number of renunciations in the first half of 2013 was up over 15 times!
The United States is the only county of the 34 members of the Organization for Economic Development that taxes its citizens no matter where they reside. Although this has been the case for quite some time, the government’s fairly recent crackdown on the reporting of foreign assets and income has made more and more Americans aware of their tax reporting responsibilities. As a result, an increasing number of the 6 million plus individuals residing aboard are apparently deciding that holding their United States citizenship is not worth the financial consequences that come with it.
The campaign to identify and tax the foreign income of United States citizens has slowly gathered force since the terrorist attacks in 2001. Foreign income reporting legislation has been on the books since 1970 when the Bank Secrecy Act of 1970 was passed, requiring the filing if an annual Report of Foreign Bank and Financial Accounts (FBAR). However, the reporting rate has historically been very low and, until recently, little was done to force compliance. All this is has change over the past few years. The government has not only stepped up its efforts to enforce the existing tax laws but has passed new legislation to supplement what was already there.
The most significant development in the area of foreign tax compliance has been the passage of the Foreign Account Tax Compliance Act (FATCA) in March of 2010. This legislation increases the disclosure requirements for United States citizens who have money in overseas accounts and for the banks that hold those accounts. Basically, FATCA requires individuals who have more than $50,000 in foreign assets to report those asserts on Form 8038. It also requires foreign banks to disclose information about their U.S. account holders or face stiff penalties for not doing so. Although the enforcement of FATCA has been postponed until July of 2014, apparently the hassle of increased compliance requirements together with the threat of steeper consequences for noncompliance has caused more and more individuals to think twice about the value of their United States citizenship.
If you have questions about the taxation and reporting of foreign assets or income, the CPAs, Enrolled Agents and Tax Attorneys at Professional Tax Resolution can provide you with the answers you are looking for. Our tax specialists have extensive experience in the area of FBAR reporting and are up to date on the current requirements for FATCA compliance. For more information about our services, visit us today at www.professionaltaxresolution.com or call us at 877.889.6527 to receive a free, no obligation consultation.